In this article we will talk about Pilonidal Sinus treatment without surgery. Discover effective non-surgical methods, lifestyle adjustments, and expert insights for optimal healing.
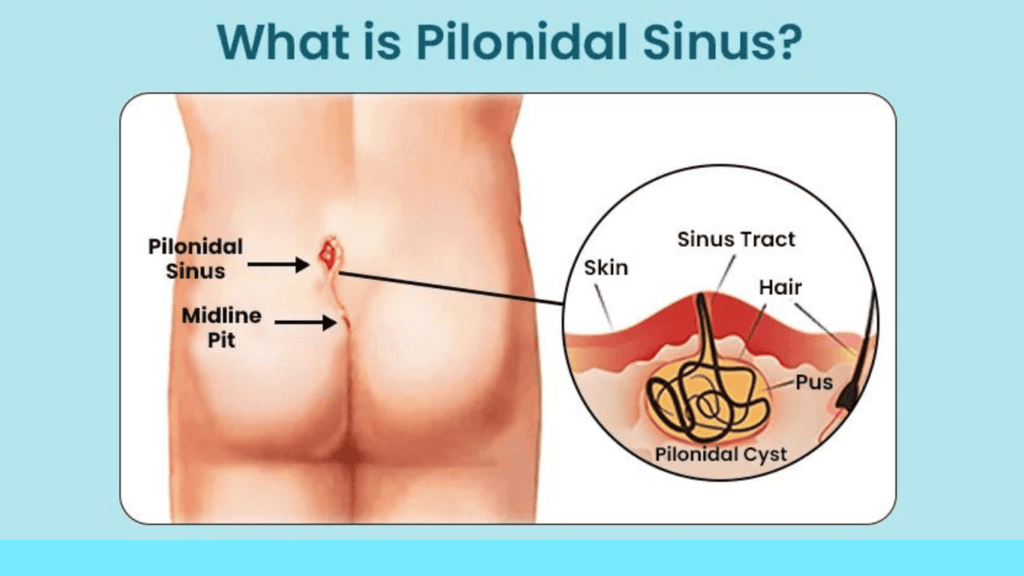
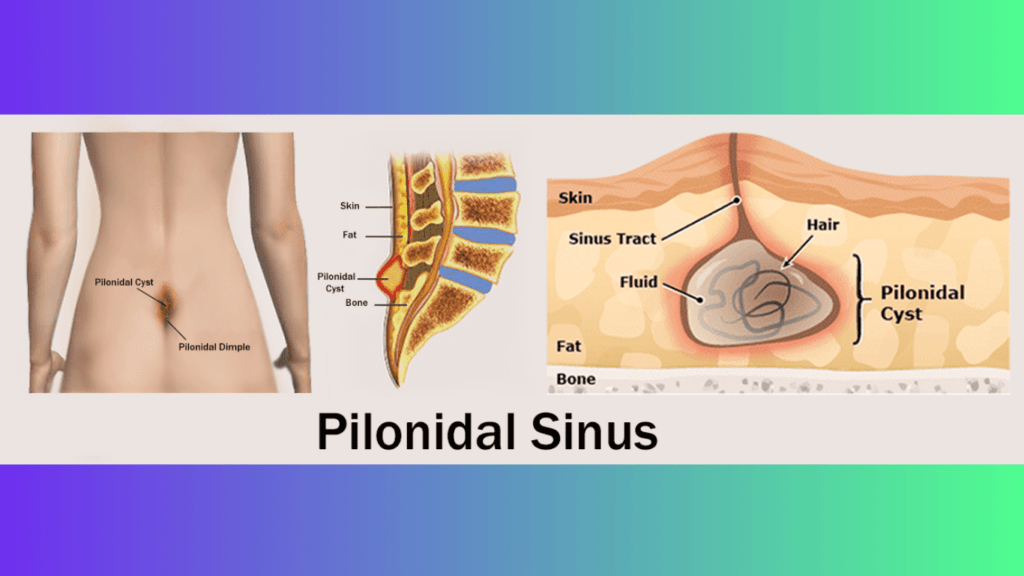
A pilonidal sinus is a small tunnel or channel that forms in the skin, usually at the top of the buttocks, near the cleft of the buttocks. This condition typically occurs when hair, dirt, or debris becomes trapped in a small opening in the skin, leading to the formation of a cyst or abscess. The term “pilonidal” is derived from Latin words meaning “hair” and “nest,” highlighting the connection to hair accumulation.
While surgery is a common approach, there are non-surgical methods and lifestyle modifications that can be explored for effective management. Here’s a comprehensive guide to pilonidal sinus treatment without surgery.
Brief explanation of the key aspects of a pilonidal sinus:
Table of Contents
- 1 Brief explanation of the key aspects of a pilonidal sinus:
- 2 Prevalence:
- 3 Common Misconceptions about Treatment Options:
- 4 Causes and Risk Factors of Pilonidal Sinus:
- 5 Typical Symptoms of Pilonidal Sinus and Its Effects on Individuals:
- 6 Traditional Surgical Approaches for Pilonidal Sinus:
- 7 Drawbacks and Potential Complications of Conventional Surgical Treatments:
- 8 Pilonidal Sinus Treatment Without Surgery: A Comprehensive Approach to Healing
- 9 Modern Non-Surgical Alternatives for Pilonidal Sinus Treatment:
- 10 Advantages and Potential Breakthroughs in Pilonidal Sinus Treatment without Surgery:
- 11 Homeopathic medicines for Pilonidal Sinus
- 12 Conclusion
1. Location: Pilonidal sinuses are commonly found at the base of the spine, just above the cleft of the buttocks. The area may develop a small dimple or pit, and infection can occur, resulting in the formation of a sinus.
2. Cause: The exact cause of pilonidal sinuses is not always clear, but it is often associated with the penetration of hair into the skin. Friction and pressure in the affected area, such as prolonged sitting or trauma, may contribute to the development of the condition.
3. Symptoms: Individuals with a pilonidal sinus may experience symptoms such as pain, swelling, redness, and drainage of pus or blood. In some cases, the area may become infected, leading to more severe symptoms.
4. Treatment: Treatment options for pilonidal sinus depend on the severity of the condition. Mild cases may respond to home care, including keeping the area clean and avoiding prolonged sitting. More severe cases may require medical intervention, such as drainage of abscesses, antibiotics for infection, or surgical procedures to remove the cyst or sinus.
5. Prevention: Preventive measures include maintaining good personal hygiene, avoiding prolonged sitting, and keeping the area dry and clean. Additionally, some individuals with a predisposition to pilonidal sinus may benefit from hair removal techniques in the affected area.
It’s important to note that pilonidal sinuses can vary in severity, and while some cases may resolve with conservative measures, others may require more extensive medical or surgical intervention. Individuals experiencing symptoms or concerns should seek medical advice for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Prevalence:
The prevalence of pilonidal sinus varies, but it is generally more common in young adults, particularly males. It is estimated that a significant number of cases occur in individuals between the ages of 15 and 30. Certain factors, such as a family history of the condition and the presence of excess body hair, may increase the likelihood of developing a pilonidal sinus.
Common Misconceptions about Treatment Options:
1. Antibiotics Alone are Sufficient:
– Misconception: Some people believe that antibiotics alone can effectively treat pilonidal sinus without surgery.
– Reality: While antibiotics may be prescribed to manage infections associated with pilonidal sinuses, they are not a standalone treatment. The primary approach often involves drainage of abscesses and, in some cases, surgical intervention to address the underlying issue.
2. Home Remedies are Always Effective:
– Misconception: There’s a belief that home remedies, such as applying creams or keeping the area clean, are always sufficient for treating pilonidal sinuses.
– Reality: Mild cases may respond to home care, but more severe or recurrent cases often require medical attention. Surgery is sometimes necessary to remove the cyst or sinus and prevent future occurrences.
3. Shaving the Area Prevents Recurrence:
– Misconception: Shaving the area around a pilonidal sinus is thought to prevent recurrence.
– Reality: While keeping the area hair-free may help reduce the risk of hair penetration and infection, it is not always a guaranteed preventive measure. Other factors, such as proper hygiene and avoiding prolonged sitting, also play crucial roles in preventing recurrence.
4. Only One Surgical Option Exists:
– Misconception: People may think that there’s only one surgical option for treating pilonidal sinuses.
– Reality: Various surgical approaches exist, ranging from simple drainage procedures to more extensive excision and closure techniques. The choice of surgical method depends on factors such as the severity of the condition and the likelihood of recurrence.
5. Prolonged Bed Rest is Necessary After Surgery:
– Misconception: Some individuals believe that prolonged bed rest is necessary after surgical treatment.
– Reality: While a short period of rest may be recommended immediately after surgery, prolonged bed rest is generally not required. Early mobilization is often encouraged to prevent complications and promote healing.
Individuals with pilonidal sinuses must consult healthcare professionals for accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment. The effectiveness of treatment options can vary based on the severity of the condition, and a personalized approach is often needed for optimal outcomes.
Best Homeopathic Medicine for Pilonidal Cyst-https://youtu.be/r3RVZc66NiY
Causes and Risk Factors of Pilonidal Sinus:
1. Hair Penetration:
– Cause: One of the primary causes of pilonidal sinus is the penetration of hair into the skin, particularly in the cleft of the buttocks.
– Risk Factor: Excess body hair, coarse hair, or hair that is tightly curled may increase the likelihood of hair penetration, leading to the development of a pilonidal sinus.
2. Friction and Pressure:
– Cause: Friction and pressure in the buttock area, often due to activities like prolonged sitting or riding a bike, can contribute to the formation of pilonidal sinuses.
– Risk Factor: Occupations or activities that involve prolonged sitting or friction in the affected area may increase the risk of developing the condition.
3. Congenital Predisposition:
– Cause: There is evidence to suggest a congenital predisposition to pilonidal sinus, indicating that some individuals may have a genetic susceptibility.
– Risk Factor: Individuals with a family history of pilonidal sinuses may be at a higher risk of developing the condition themselves.
4. Poor Hygiene:
– Cause: Lack of proper hygiene in the buttock area can contribute to the accumulation of dirt, sweat, and bacteria, creating an environment conducive to the development of pilonidal sinuses.
– Risk Factor: Poor hygiene practices increase the risk of infection and inflammation in the affected area.
5. Obesity:
– Cause: Obesity is identified as a risk factor for pilonidal sinuses, possibly due to increased pressure and friction in the buttock area.
– Risk Factor: Individuals with obesity may have a higher likelihood of developing pilonidal sinuses compared to those with normal body weight.
6. Age and Gender:
– Cause: Pilonidal sinuses are more common in young adults, particularly males.
– Risk Factor: The condition is often diagnosed in individuals between the ages of 15 and 30, and males are more frequently affected than females.
7. Inactive Hair Follicles:
– Cause: Hair follicles that are not actively growing may become blocked and prone to infection, contributing to the development of pilonidal sinuses.
– Risk Factor: Inactivity or dormancy of hair follicles may increase the risk, especially in areas where the hair is tightly curled.
Understanding the causes and risk factors can help individuals take preventive measures and seek early intervention if they notice symptoms associated with pilonidal sinus treatment without surgery. Maintaining good personal hygiene, avoiding prolonged sitting, and addressing risk factors can contribute to reducing the likelihood of developing this condition.
Typical Symptoms of Pilonidal Sinus and Its Effects on Individuals:
1. Pain and Tenderness:
– Symptoms: Individuals with pilonidal sinus often experience pain and tenderness in the affected area, especially when sitting or with any pressure on the lower back.
– Effects: The pain can range from mild discomfort to severe pain, impacting daily activities and quality of life. It may lead to difficulty sitting for extended periods.
2. Swelling and Redness:
– Symptoms: Swelling and redness around the pilonidal sinus are common, indicating inflammation and infection in the affected area.
– Effects: Swelling can contribute to increased pain and discomfort, while redness may be a visible sign of the inflammatory process. In some cases, the area may feel warm to the touch.
3. Pus or Blood Drainage:
– Symptoms: Pus or blood drainage from the pilonidal sinus is a common symptom, especially when the sinus becomes infected.
– Effects: Drainage may lead to soiling of clothing and can be socially embarrassing. The presence of pus indicates an active infection that may require medical attention.
4. Fever and Malaise:
– Symptoms: Systemic symptoms such as fever and a general feeling of malaise (unwell) may occur with an infected pilonidal sinus.
– Effects: Fever and malaise are signs that the infection may be spreading, and medical attention is crucial to prevent complications.
5. Recurrent Abscess Formation:
– Symptoms: Recurrent formation of abscesses in the same area is common in individuals with pilonidal sinuses.
– Effects: The recurrence of abscesses can lead to a chronic condition, causing ongoing pain and discomfort. It may also necessitate repeated medical interventions or surgical procedures.
6. Impaired Daily Activities:
– Symptoms: The pain and discomfort associated with pilonidal sinuses can impair daily activities, especially those that involve sitting for extended periods.
– Effects: Individuals may find it challenging to engage in work, school, or recreational activities that require prolonged sitting, affecting their overall quality of life.
7. Psychosocial Impact:
– Symptoms: The visible symptoms and the recurrent nature of pilonidal sinuses can have a psychosocial impact on individuals.
– Effects: Embarrassment, self-consciousness, and anxiety about the condition may affect social interactions and mental well-being. Seeking support from healthcare professionals can help address these aspects of pilonidal sinus treatment without surgery.
Understanding the typical symptoms and effects of pilonidal sinus is essential for prompt diagnosis and appropriate management. Seeking medical advice for proper treatment, which may include drainage of abscesses, antibiotics, or surgical intervention, can help alleviate symptoms and prevent complications.
Traditional Surgical Approaches for Pilonidal Sinus:
Several conventional surgical treatments are used to address pilonidal sinuses, ranging from simple procedures to more extensive interventions. The choice of surgery depends on the severity of the condition and the individual patient. Common surgical treatments include:
1. Incision and Drainage (I&D):
– Description: This is a relatively simple procedure where the surgeon makes an incision to drain the abscess or cyst, removing accumulated pus and debris.
– Drawbacks: While I&D is effective for acute abscesses, it may not prevent recurrent pilonidal sinus. It is often used as a temporary measure.
2. Excision and Primary Closure:
– Description: The surgeon removes the entire pilonidal sinus, including the cyst and the surrounding tissue, and then closes the wound with stitches.
– Drawbacks: This method has a risk of wound breakdown and infection. Recovery may be more prolonged, and the risk of recurrence can still exist.
3. Open Wound Healing:
– Description: The surgeon removes the sinus and leaves the wound open, allowing it to heal gradually from the inside out.
-Drawbacks: Open wound healing requires regular dressing changes and may take a longer time to heal. There is also a risk of infection during the healing process.
4. Flap Procedures:
– Description: Flap procedures involve using nearby tissue to cover the wound after the sinus is removed. Common flap techniques include the Karydakis procedure and the Limberg flap.
– Drawbacks: Flap procedures are more complex and may be associated with a longer recovery period. They are usually reserved for recurrent or complex cases.
5. Laser Hair Removal:
– Description: Laser hair removal can be used to reduce hair in the affected area, aiming to prevent future hair penetration and recurrence.
– Drawbacks: This approach is not always curative on its own, and it may need to be combined with other surgical or non-surgical treatments.
Drawbacks and Potential Complications of Conventional Surgical Treatments:
1. Recurrence:
– Drawback: Despite surgical intervention, pilonidal sinuses may recur, especially if underlying risk factors such as excess body hair and poor hygiene are not addressed.
2. Wound Complications:
– Complications: Wound complications can include infection, delayed healing, and wound breakdown. Open wound healing methods are particularly prone to these issues.
3. Pain and Discomfort:
– Drawback: Postoperative pain and discomfort are common, and recovery may involve limitations on activities such as sitting.
4. Scarring:
– Complication: Surgical procedures can result in visible scars, and the extent of scarring depends on the type of surgery performed.
5. Bleeding:
– Complication: Surgical procedures carry a risk of bleeding, which may require further intervention if significant.
6. Infection:
– Complication: Infections can occur at the surgical site, leading to increased pain, swelling, and the need for additional treatment.
7. Anesthesia Risks:
– Complication: Any surgical procedure involving anesthesia carries inherent risks, including adverse reactions or complications.
8. Psychosocial Impact:
– Drawback: Surgery and the associated recovery period can have psychosocial effects, including anxiety, embarrassment, or disruptions to daily life.
It’s important for individuals considering for pilonidal sinus treatment without surgery to discuss potential drawbacks and complications with their healthcare provider. Each case is unique, and the choice of treatment should be tailored to the individual’s condition and medical history.
Pilonidal Sinus Treatment Without Surgery: A Comprehensive Approach to Healing
While surgery is a common intervention, several non-surgical approaches can be explored for effective treatment and management.
1. Antibiotics:
– Usage: In cases of infection, antibiotics may be prescribed to control and eliminate bacterial growth. Consultation with a healthcare professional is advisable for appropriate recommendations.
– Effectiveness: Antibiotics can help reduce inflammation and prevent the infection from worsening.
2. Pilonidal Sinus Baths:
– Procedure: Regular warm baths, especially with added Epsom salt, can promote cleanliness and drainage.
– *Effectiveness: Warm baths aid in keeping the area clean, minimizing the risk of infection, and facilitating natural drainage and helpful for pilonidal sinus treatment without surgery.
3. Topical Treatments:
– Application: The use of topical ointments or creams containing antibacterial or anti-inflammatory agents.
– *Effectiveness:* Topical treatments can provide relief from symptoms and aid in the healing process.
4. Laser Hair Removal: (hair removal pilonidal cyst)
– Procedure: Laser therapy can be used to remove hair around the affected area, reducing the risk of hair follicle penetration.
– Effectiveness: By preventing hair ingrowth, laser hair removal aims to minimize the recurrence of pilonidal sinus.
5. Pilonidal Sinus Irrigation:
– Method: Flushing the sinus with a saline solution using a syringe or a specialized tool.
– Effectiveness: Irrigation helps cleanse the sinus tract, promoting healing and preventing infection.
6. Dressings and Packing:
– Application: Sterile dressings and packing materials can be used to absorb drainage and maintain cleanliness.
– Effectiveness: Proper dressings assist in preventing bacterial contamination and support the healing process.
7. Pain Management:
– Approach: Over-the-counter pain relievers or prescribed medications to manage pain and discomfort.
– Effectiveness: Pain management is essential for enhancing patient comfort during the healing process.
8. Physical Activity Modification:
– Recommendation: Avoid prolonged periods of sitting and maintain good personal hygiene.
– Effectiveness: Lifestyle adjustments can reduce friction and pressure on the affected area, promoting healing.
9. Healthy Diet:
– Emphasis: A diet rich in fiber to prevent constipation, which can exacerbate symptoms.
– Effectiveness: Dietary modifications contribute to overall well-being and support the body’s healing mechanisms.
10. Regular Follow-ups:
– Importance: Regular check-ups with a healthcare professional to monitor progress and make adjustments to the treatment plan.
– Effectiveness: Timely assessments ensure that the chosen non-surgical interventions are effective and adjustments can be made if needed.
11. Tea Tree Oil:
– Tea tree oil has natural antibacterial properties. Diluted tea tree oil can be applied topically to aid in preventing infections.
12. Elevated Seating:
– Use a cushion or a specially designed seat to elevate the buttocks when sitting. This can reduce pressure on the pilonidal sinus and aid in healing.
13. Weight Management:
– Maintaining a healthy weight reduces pressure on the affected area, contributing to improved healing and preventing recurrence.
While these non-surgical approaches can be beneficial for some individuals with pilonidal sinus, it’s crucial to consult with a healthcare professional for personalized guidance and a comprehensive treatment plan tailored to the specific needs of each patient.
Modern Non-Surgical Alternatives for Pilonidal Sinus Treatment:
Advancements in medical technology have led to the development of non-surgical alternatives for the treatment of pilonidal sinus. These options aim to provide effective management while minimizing the drawbacks associated with traditional surgical interventions. Here’s an overview of some modern non-surgical alternatives:
1. Laser Hair Removal: (laser pilonidal sinus)
– Overview: Laser hair removal is a non-surgical method that targets and destroys hair follicles in the affected area, reducing the risk of hair penetration.
– Advantages: It can be a preventive measure to decrease the recurrence of pilonidal sinuses. The procedure is generally well-tolerated, and patients can resume normal activities quickly.
2. Minimally Invasive Techniques:
– Overview: Procedures such as minimally invasive video-assisted techniques or endoscopic pilonidal sinus treatment involve the use of small incisions and specialized tools for sinus removal.
– Advantages: These techniques typically result in smaller wounds, reduced postoperative pain, and faster recovery compared to traditional open procedures.
3. Radiation Therapy:
– Overview: Radiation therapy is sometimes used to treat pilonidal sinuses. Low-dose radiation is applied to the affected area to reduce hair growth and promote healing.
– Advantages: It can be an alternative for individuals who may not be suitable candidates for surgery. However, the use of radiation therapy in pilonidal sinus treatment is not yet widely adopted.
4. Topical Therapies:
– Overview: Topical applications of certain medications or solutions may be used to promote wound healing and reduce inflammation in the pilonidal sinus.
– Advantages: Non-invasive and can be used as part of a conservative treatment approach for milder cases.
Advantages and Potential Breakthroughs in Pilonidal Sinus Treatment without Surgery:
1. Reduced Invasiveness:
– Advantage: Modern non-surgical alternatives often involve less invasive techniques, resulting in smaller wounds, reduced pain, and faster recovery compared to traditional open surgeries.
2. Preventive Measures:
– Advantage: Some non-surgical options, such as laser hair removal, focus on preventing hair penetration and recurrence, addressing the root cause of pilonidal sinuses.
3. Customized Treatment Plans:
– Advantage: Healthcare providers can tailor treatment plans to the individual, considering factors such as the severity of the condition, the patient’s preferences, and medical history.
4. Outpatient Procedures:
– Advantage: Many non-surgical procedures can be performed on an outpatient basis, reducing the need for hospitalization, and allowing for a quicker return to normal activities.
5. Ongoing Research and Innovation:
– Potential Breakthroughs: Ongoing research aims to explore innovative treatments, including biological therapies, advanced wound healing techniques, and personalized approaches based on genetic factors.
6. Patient-Centered Care:
– Advantage: Non-surgical alternatives contribute to a more patient-centered approach, offering choices that align with individual preferences, especially for those who prefer non-invasive or minimally invasive options.
While non-surgical alternatives show promise in the management of pilonidal sinuses, it’s essential to note that the effectiveness of these approaches can vary among individuals, and further research is needed to establish their long-term outcomes. Patients should consult with healthcare professionals to determine the most suitable treatment plan based on their specific condition and needs.
Homeopathic medicines for Pilonidal Sinus
It’s important to note that while some people may choose to explore complementary and alternative therapies, such as homeopathic medicines, for various conditions, the scientific evidence supporting the efficacy of homeopathy in treating pilonidal sinus without surgery is broad. Pilonidal sinus is a medical condition, and conventional medical treatments, including surgical interventions, are often recommended by healthcare professionals based on the severity of the condition.
If someone is considering homeopathic remedies for pilonidal sinus, they should do so under the guidance and supervision of a qualified homeopathic practitioner or a healthcare professional. Homeopathy is a system of medicine that involves using highly diluted substances to stimulate the body’s healing mechanisms.
Here are a few homeopathic remedies that have been traditionally suggested for pilonidal sinus:
1. Silicea (Silica):
– Indication: Silicea is often recommended for chronic suppurations and conditions involving the formation of abscesses, which may apply to some cases of pilonidal sinus.
– Dosage: The dosage can vary, and it should be prescribed by a qualified homeopathic practitioner based on an individual’s symptoms.
2. Myristica Sebifera (Myristica):
– Indication: Myristica is associated with suppuration and the promotion of drainage, and it has been historically used for abscesses and boils.
– Dosage: As with any homeopathic remedy, the dosage should be individualized and determined by a qualified practitioner.
3. Hepar Sulphuris Calcareum (Hepar Sulph):
– Indication: Hepar Sulph is often considered when there is a tendency for abscess formation and inflammation.
– Dosage: The appropriate dosage should be determined by a homeopathic practitioner based on the specific symptoms.
Homeopathic medicines are based on individuality. Before considering any homeopathic remedy, individuals should consult with their healthcare provider for Pilonidal Sinus treatment without surgery, preferably one who is knowledgeable about homeopathy, to discuss their symptoms and explore appropriate treatment options.
In general, conventional medical treatments, such as surgical interventions, are commonly recommended for pilonidal sinus based on their proven efficacy. Homeopathic treatments, if chosen, should be pursued as complementary to conventional care and under the guidance of a qualified healthcare professional.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the comprehensive guide on Pilonidal Sinus Treatment Without Surgery provides valuable insights into the nature, symptoms, causes, and treatment options for this condition. Pilonidal sinus, characterized by the formation of a small tunnel or channel at the base of the spine, often poses challenges due to its recurrence and potential complications.
While surgery remains a common approach, the article emphasizes non-surgical methods and lifestyle adjustments as effective alternatives for managing pilonidal sinuses. It highlights the importance of maintaining good personal hygiene, avoiding prolonged sitting, and exploring various non-surgical interventions.
The prevalence of pilonidal sinus, especially among young adults, underscores the need for awareness and early intervention. The article dispels common misconceptions about treatment options, emphasizing the individualized nature of care and the multifaceted approach required for optimal outcomes.
Traditional surgical treatments, ranging from incision and drainage to flap procedures, are discussed with a focus on potential drawbacks and complications. This balanced overview prepares individuals for informed discussions with healthcare providers when considering surgical interventions.
The article also delves into modern non-surgical alternatives, showcasing advancements such as laser hair removal, minimally invasive techniques, and topical therapies. The advantages of reduced invasiveness, customized treatment plans, and ongoing research are highlighted, providing hope for improved outcomes and patient-centered care.
Additionally, the discussion on homeopathic medicines acknowledges the interest in complementary approaches while emphasizing the importance of consulting qualified practitioners. The limitations of scientific evidence for homeopathy in pilonidal sinus treatment are recognized, reinforcing the significance of an integrated approach with conventional medical guidance.
The conclusion encapsulates a comprehensive approach to pilonidal sinus treatment without surgery, emphasizing the need for personalized care, ongoing research, and the exploration of modern non-surgical alternatives. It encourages individuals to seek timely medical advice, fostering a proactive stance in managing this challenging condition.





[…] What is Pilonidal Sinus? […]