Today we will discuss about Meningitis Precautions and all the ways to protect from Meningitis.
Meningitis Precautions: Protecting Yourself and Others
Table of Contents
- 1 Meningitis Precautions: Protecting Yourself and Others
- 2 Understanding Meningitis Precautions
- 3 Importance of Meningitis Precautions
- 4 Vaccination Against Meningitis
- 5 Types of Meningitis Vaccines
- 6 Who Should Get Vaccinated?
- 7 Maintaining Hygiene
- 8 Avoiding Close Contact
- 9 Boosting Immunity
- 10 Recognizing Symptoms
- 11 Precautions for Specific Age Groups
- 12 Precautions for Travelers
- 13 Preventing Meningitis Outbreaks
- 14 Caring for Meningitis Patients
- 15 Educational Campaigns and Awareness
- 16 Common Misconceptions About Meningitis
- 17 Conclusion
- 18 FAQs about Meningitis Precautions
Meningitis is a severe infection that leads to inflammation of the protective membranes surrounding the brain and spinal cord. It can be caused by bacteria, viruses, or fungi, with bacterial meningitis being the most severe form. While meningitis can affect anyone, certain precautions can help reduce the risk of infection and its spread.
Understanding Meningitis Precautions
Meningitis precautions are essential measures taken to prevent the occurrence and transmission of meningitis. These precautions are crucial for maintaining public health and minimizing the impact of meningitis outbreaks.
Importance of Meningitis Precautions
Meningitis can spread rapidly in communities, especially in crowded settings such as schools, dormitories, and healthcare facilities. By implementing precautions, individuals can protect themselves and others from contracting and spreading the infection.
Vaccination Against Meningitis
Vaccination is one of the most effective ways to prevent meningitis. There are different types of vaccines available to protect against bacterial meningitis, including meningococcal, pneumococcal, and Hib vaccines.
Types of Meningitis Vaccines
– Meningococcal vaccine: Protects against meningococcal bacteria, which are a common cause of bacterial meningitis.
– Pneumococcal vaccine: Guards against pneumococcal bacteria, which can cause pneumococcal meningitis.
– Hib vaccine: Prevents Haemophilus influenzae type b (Hib) infection, a leading cause of bacterial meningitis in young children.
Who Should Get Vaccinated?
Vaccination against meningitis is recommended for individuals of all ages, with specific vaccination schedules tailored to different age groups and risk factors. Infants, children, adolescents, college students, travelers to high-risk areas, and individuals with certain medical conditions may require meningitis vaccination.
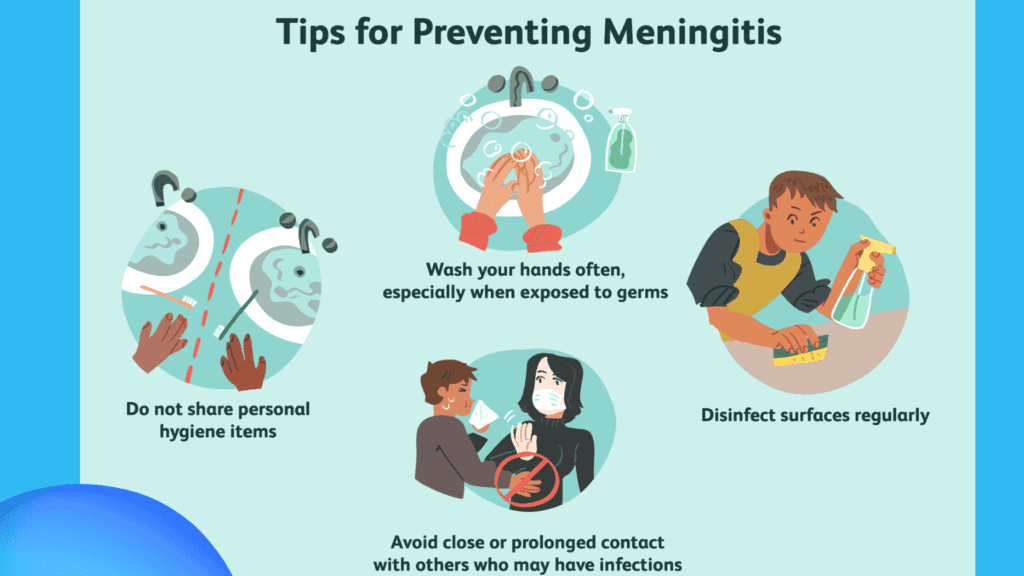
Maintaining Hygiene
Maintaining good hygiene practices is essential for preventing the spread of meningitis-causing pathogens.
a. Hand Hygiene
– Wash your hands regularly with soap and water for a minimum of 20 seconds, particularly after coughing, sneezing, or coming into contact with surfaces.
– If soap and water are unavailable, utilize alcohol-based hand sanitizers.
b. Respiratory Hygiene
– When you feel the urge to cough or sneeze, remember to shield your mouth and nose with either a tissue or your elbow, ensuring to prevent the spread of germs to those around you.
– Dispose of used tissues properly.
– It’s advisable to maintain a safe distance from individuals who are displaying signs of illness, reducing the risk of potential exposure to contagious pathogens.
Avoiding Close Contact
Limiting close contact with individuals who have meningitis or respiratory infections is crucial for preventing transmission.
a. Limiting Exposure
– Avoid sharing personal items such as utensils, drinks, and cosmetics.
– Stay away from crowded places when possible.
– Follow public health guidelines during outbreaks or epidemics.
b. Social Distancing Measures
– Maintain a safe distance from individuals who are sick, especially if they have respiratory symptoms.
– Avoid large gatherings or events where the risk of transmission is higher.
Boosting Immunity
Strengthening the immune system can help reduce the risk of meningitis and other infections.
a. Healthy Lifestyle Practices
– Get an adequate amount of sleep each night.
– Exercise regularly to improve overall health and immunity.
– Control stress by practicing relaxation techniques like yoga or meditation.
b. Nutritious Diet
– Maintain a well-balanced diet comprising fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins.
– Keep your body well-hydrated by regularly drinking an adequate amount of water throughout each day, ensuring optimal hydration levels for overall health and well-being.
Recognizing Symptoms
Being able to recognize the early symptoms of meningitis is crucial for seeking prompt medical attention.
a. Early Signs of Meningitis
1- Fever
2- Headache
3- Stiff neck
4- Nausea and vomiting
5- Sensitivity to light
b. Seeking Medical Attention Promptly
If you or someone you know develops symptoms of meningitis, seek medical help immediately. Early diagnosis and treatment are essential for preventing complications and reducing the risk of transmission.
Precautions for Specific Age Groups
Different age groups may have unique considerations when it comes to meningitis precautions.
a. Meningitis Precautions for Infants and Children
– Ensure that infants receive recommended vaccinations on schedule.
– Practice good hygiene around newborns and young children.
– Be aware of signs of illness and seek medical advice if symptoms occur.
b. Meningitis Precautions for Adults
– Stay up-to-date with recommended vaccinations, especially if traveling to high-risk areas.
– Practice good hygiene habits and avoid close contact with sick individuals.
– Be aware of the symptoms of meningitis and seek medical attention if necessary.
Precautions for Travelers
Travelers to regions where meningitis is prevalent should take additional precautions to protect themselves from infection.
a. High-Risk Destinations
– Research destinations for potential health risks, including meningitis outbreaks.
– Consult with a healthcare provider before traveling to receive appropriate vaccinations and advice.
b. Pre-Travel Consultation
– Schedule a pre-travel consultation with a healthcare professional to discuss vaccination recommendations and travel health precautions.
– Follow recommended guidelines for preventing respiratory infections and practicing good hygiene while traveling.
Preventing Meningitis Outbreaks
Public health measures play a crucial role in preventing meningitis outbreaks and controlling the spread of infection within communities.
Public Health Measures
– Implement vaccination programs targeting high-risk populations.
– Conduct surveillance and monitoring of meningitis cases to detect outbreaks early.
– Provide education and resources to healthcare providers and the public about meningitis prevention and control.
Caring for Meningitis Patients
Proper care and management of individuals with meningitis are essential for preventing further transmission and ensuring positive outcomes.
a. Isolation Precautions
— Isolate individuals diagnosed with meningitis to prevent the spread of infection to others.
— Follow infection control protocols to minimize the risk of transmission in healthcare settings.
b. Close Monitoring
– Monitor patients closely for signs of complications or deterioration in health.
– Provide supportive care, including hydration, pain management, and fever control.
Educational Campaigns and Awareness
Raising awareness about meningitis and promoting preventive measures through educational campaigns can help reduce the burden of the disease.
a. Community Outreach Programs
– Organize educational events and workshops to inform the public about meningitis risks and prevention strategies.
– Distribute educational materials, such as brochures and flyers, in schools, workplaces, and community centers.
b. Educational Materials and Resources
– Develop informative resources, such as websites and mobile apps, to provide access to reliable information about meningitis and vaccination.
– Collaborate with healthcare professionals, advocacy groups, and government agencies to disseminate educational materials effectively.
Common Misconceptions About Meningitis
Addressing misconceptions and clarifying facts about meningitis can help dispel myths and promote accurate understanding.
a. Dispelling Myths
– Meningitis is not solely caused by cold weather or drafts.
– Meningitis vaccines are safe and effective in preventing infection.
b. Clarifying Facts
– Meningitis can be caused by bacteria, viruses, or fungi.
– Prompt medical treatment is essential for meningitis management and prevention of complications.
Conclusion
Meningitis is a serious infectious disease that requires proactive measures to prevent its occurrence and transmission. By following meningitis precautions, individuals can protect themselves and others from infection and contribute to public health efforts to control the spread of the disease.
FAQs about Meningitis Precautions
1. Q: Can meningitis be prevented through vaccination alone?
A: While vaccination is a crucial preventive measure, other precautions such as maintaining hygiene and avoiding close contact with sick individuals are also important.
2. Q: Who is at higher risk of developing meningitis?
A: Infants, young children, adolescents, college students living in dormitories, travelers to high-risk areas, and individuals with certain medical conditions are at increased risk of meningitis.
3. Q: How effective are meningitis vaccines?
A: Meningitis vaccines are highly effective in preventing infection and reducing the risk of severe complications. However, no vaccine provides 100% protection, so it’s important to continue practicing other preventive measures.
4. Q: Are there any side effects associated with meningitis vaccines?
A: Most people experience mild side effects such as redness or swelling at the injection site or mild fever. Serious side effects are rare.
5. Q: What should I do if I suspect someone has meningitis?
A: If you suspect someone has meningitis based on their symptoms, seek medical help immediately. Prompt diagnosis and treatment are essential for a favorable outcome.